Understanding how much is Job Seekers Allowance is essential for anyone navigating unemployment in the UK. Whether you’re between jobs or recently made redundant, Job Seekers Allowance (JSA) can provide essential financial support while you actively seek employment. This benefit, administered by the Department for Work and Pensions (DWP), ensures that eligible individuals maintain financial stability and continue to build their National Insurance record during their job search.
This comprehensive guide explains the eligibility rules, how JSA is calculated, how it compares with Universal Credit, and how you can maximize your claim. Whether you’re under 25 or over, single or partnered, this post will help you understand every detail of how much Job Seekers Allowance is and how it supports your journey back into employment.
What is Job Seekers Allowance?
Job Seekers Allowance (JSA) is a DWP-administered benefit aimed at providing temporary income for individuals actively seeking work in Great Britain (England, Scotland, Wales).
- Purpose: It offers financial support, job-search obligations, and National Insurance credits.
- Benefit for claimants: It ensures continuity of financial aid and helps maintain contributions toward the State Pension.
What are the two main types of Job Seekers Allowance?
- Legacy JSA
- Includes two sub-types:
- Income-based JSA: means-tested, dependent on household income and savings.
- Contribution-based JSA: paid to those qualifying via NI contributions, but gradually being phased out in favor of Universal Credit
- Includes two sub-types:
- New-style JSA
- Fully contribution-based; eligibility is determined purely by Class 1 NI contributions over the past two tax years—not means-tested
- Paid fortnightly for up to 182 days, with Class 1 NI credits accruing to protect pension rights
Who can claim Job Seekers Allowance in Great Britain?
To qualify for new-style JSA, claimants must:
- Be in the age range of 18 to the State Pension age.
- Live in England, Scotland, or Wales.
- possess credits or have made adequate Class 1 NI contributions throughout the previous two tax years.
- Be accessible and actively looking for job, and work fewer than 16 hours each week.
- Not be in a trade dispute or incapable of work due to illness (in which case ESA is more appropriate).
Legacy income-based JSA has stricter means tests (e.g., savings under £16,000)
What are the eligibility rules for Job Seekers Allowance?

The purpose of the JSA is to assist those who are actively seeking employment. Although there are other forms of JSA, the most popular one nowadays is the contribution-based “New Style” JSA. Here’s a breakdown of the general eligibility rules.
How old do you need to be to claim JSA?
To qualify for JSA, you must:
-
Be at least 18 but not yet eligible for the State Pension.
-
For those aged 18 to 24, a lower rate is paid
-
For those aged 25 or older, a higher rate applies
Note: In some circumstances, 16–17-year-olds may qualify (e.g. if they are estranged or in severe financial hardship), but this is rare and usually involves special support arrangements.
What residency and labor‑market conditions apply?
Residency and Right to Reside
Applicants must:
-
Be habitually resident in Great Britain (i.e., England, Scotland, or Wales)
-
Possess the legal right to live and work in the United Kingdom
-
Be free from immigration restrictions (with few exceptions)
Labor Market Availability
To remain eligible, you must:
-
Be actively seeking work each week and provide proof of your efforts
-
Be available to work full-time (usually interpreted as around 35 hours per week)
-
Agree to a Claimant Commitment with your Work Coach at Jobcentre Plus
If you’re only available for part-time work due to valid reasons—such as caring for a dependent, having a disability, or specific health needs—you may still be eligible, but your commitment will be adjusted accordingly.
Part-Time Work and JSA
-
You may work up to 16 hours per week and still receive JSA.
-
Earnings above a certain threshold will reduce your JSA payment.
-
Accurate declaration of all earnings and hours is necessary to prevent overpayments or penalties.
If you earn too much or increase your working hours beyond the limit, your JSA may stop entirely.
Additional Requirements and Considerations
-
You must attend regular appointments at the Jobcentre to review your job search activities
-
Failure to meet agreed conditions (e.g., missing interviews, refusing work) may result in a sanction—a temporary reduction or suspension of your JSA
-
You must not be in full-time education (unless specific exemptions apply, such as short training courses that enhance employability)
How does New-style JSA differ from Legacy JSA?
| Feature | Legacy JSA | New-style JSA |
| Means-tested | Yes (income & savings) | No |
| £ cap on savings | £16,000 | No effect on claim |
| Payment length | Varies, until job found | Up to 182 days (approx. 6 months) |
| NI credits | Yes | Paid (Class 1) |
| Payment frequency | Fortnightly | Fortnightly |
New-style offers faster access and greater simplicity, particularly for those without household income constraints.
Can I claim JSA if I’m on Universal Credit?
- It is possible to receive both Universal Credit and contribution-based JSA.
- JSA payments are counted toward your UC assessment, potentially reducing UC entitlement.
- JSA is paid fortnightly, while UC is monthly in arrears—understanding both cycles is key to financial planning.
How much can I get each week in Job Seekers Allowance?
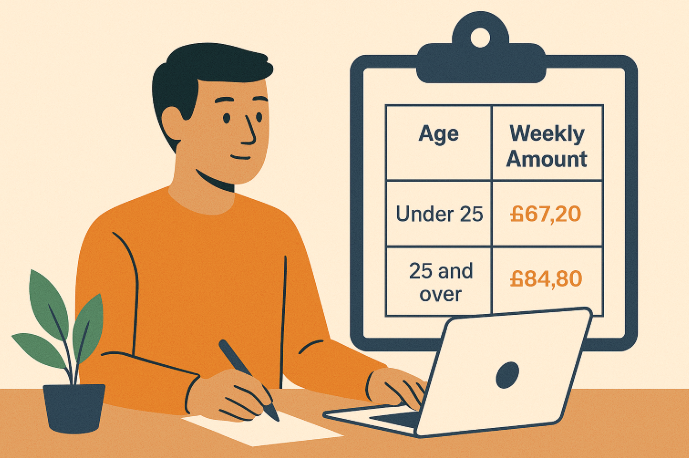
What are the current JSA weekly rates by age and type?
New-style/Contribution-based JSA (2025–26):
-
- Under 25: £72.90/week
- 25 and over: £92.05/week
- Legacy income-based JSA (couples): rates vary based on age and household composition; average couple rate ~£144.65/week .
What ancillary payments might increase my JSA?
Premiums that can augment JSA include:
- Disabled Living Allowance or Severe Disability Premium
- Dependent child additions
- Carer Allowance
- Pensioner Premium
These are added on top of the base rate and are not means-tested in new-style JSA.
How are Job Seekers Allowance payments calculated?

How does your income affect your JSA amount?
New-style JSA ignores partner income/savings, but:
-
- Earnings are partially disregarded: the first £5 + 10% of remaining weekly earnings reduce entitlement
- Pension income above £50/week also leads to deductions.
- Legacy JSA deducts all income above personal allowances and savings effects (£1/week for every £250 over £6,000 up to £16,000)
What happens during the JSA “initial assessment period”?
- A 7-day “waiting period” applies initially; no payments are made for those days
- After that, allow up to 14 days for the first payment; it may be less than the full fortnightly amount if applied partway through the cycle .
How do deductions, sanctions or overpayments change JSA?
- Sanctions may suspend benefits when claimant fails job-search commitments:
- First lower-level offence = 7 days + delay; repeated may last 28 days or more.
- Misconduct or higher-level voluntary departure: 13–26 weeks
- Overpayments (e.g. undisclosed income or late notification of change) are reclaimed per DWP debt recovery rules.
- Deductions may occur for court-ordered payments or utility arrears directly from JSA.
How much is new style JSA?
-
Weekly payment depends on your age:
-
If you’re under 25, you can get up to £72.90 per week.
-
If you’re 25 or older, the rate goes up to £92.05 per week.
-
-
You’re paid every two weeks: The money is usually deposited into your bank account once every fortnight.
-
You can receive it for up to 6 months: The maximum claim period is 182 days, as long as you continue to meet the eligibility requirements.
-
No payment for the first 7 days: There’s a waiting period at the start of your claim where no money is paid—this is standard for most new claims.
-
Part-time work or pensions may reduce your payment: If you’re earning a small income or getting a pension, your JSA amount could be adjusted accordingly.
-
Based on National Insurance, not income: Your entitlement is based on your recent NI contributions, so things like your partner’s income or savings won’t usually affect your payment.
How does Job Seekers Allowance compare with Universal Credit?
What are the main differences in payments?
| Feature | JSA | Universal Credit (UC) |
| Calculation basis | NI contributions or means-tested | Mean-tested household benefit |
| Under-25 rate | £72.90/week | ~£92/week standard allowance |
| Payment frequency | Bi‑weekly | Monthly in arrears |
| Initial waiting time | 7-day wait + 14-day delay | ~5 weeks to first full payment |
| Premiums | Yes—dependents, disability, etc. | Yes—housing, family, childcare, disability |
| Sanctions | Significant duration (4–26 weeks) | Also applies, but varied structure |
Which one is better for different claimants?
New‑style JSA suits those with sufficient NI contributions and wanting:
-
- Bi‑weekly payments
- Simpler, faster case processing
- NI credits for pensions
- Shorter claim window (6 months)
Universal Credit benefits families needing housing support or childcare help, but has a longer wait and monthly payments.
Can you claim both JSA and UC at the same time?
It is possible to claim both UC and contribution-based JSA. But:
- JSA payments are treated as income and reduce UC award on a £1-for-£1 basis.
- UC is disbursed after a month in arrears, while JSA pays every fortnight.
- Many claimants choose UC alone when household needs (e.g. housing, family) outweigh the benefits.
What are common barriers or conditions when claiming JSA?
What is the “initial assessment period” and how long is it?
- You must complete 7 consecutive waiting days; no payments during these first days.
- Next, your first payment arrives in approximately two weeks (bi-weekly cycle)
- The new rule restoring 7 waiting days (from previous 3 days) came into effect in October 2025 .
How can sanctions or overpayments affect your weekly rate?
- Sanctions can stop or reduce JSA for 7 days to 26 weeks depending on severity.
- Overpayment recovery may be by deductions from future payments, requiring debt management planning.
What happens if you withdraw your claim or change circumstances?
- You must report changes immediately (e.g. work, savings, address) via GOV.UK or Jobcentre.
- Failure to do so can lead to overpayments, sanctions or debts .
- In case of sanction or disagreement, mandatory reconsideration must be requested within 1 month (14 days extra after written reasons).
How do you apply for Job Seekers Allowance in Great Britain?

What documents and evidence will you need?
- National Insurance number
- Bank/building society account details
- Pension statements, if applicable (occupational, private, inherited pensions)
- Payslips or proof of any part-time work.
- Work history for the previous six months (employers, dates)
Should you apply online, by phone, or in person?
- New-style JSA: apply online via GOV.UK; phone (0800 055 6688) or Job centre for assistance .
- Legacy income-based JSA: often conducted over the phone or in-person at Job Centres; some, but not all, do it online.
How long will it take to receive your first payment?
- You’ll receive an invitation for a work coach interview within 5 working days
- After that: 7 waiting days, then about 14 days until the first payment—total ~21 days.
- Payments continue every 2 weeks thereafter
Can I claim JSA if I quit my job?
-
Quitting voluntarily can affect your claim: If you leave your job without a good reason, your JSA claim may be delayed or denied for a period, typically up to 13 weeks.
-
You must explain your reasons: To be eligible, you’ll need to show you had a valid reason for leaving—such as unsafe working conditions, harassment, or caring responsibilities.
-
Evidence strengthens your claim: Providing supporting documents, like a doctor’s note or a formal grievance, can help prove that leaving your job was justified.
-
JSA eligibility criteria still apply: You must still meet the general conditions for JSA, such as being available for work, actively seeking a job, and being under State Pension age.
-
You might be referred to a decision maker: If you left your job voluntarily, your case will likely be reviewed by a DWP decision maker who will assess whether a sanction is appropriate.
-
Consider New Style JSA or Universal Credit: Depending on your National Insurance contributions and financial circumstances, you may qualify for New Style JSA or need to apply for Universal Credit instead.
What are recent changes or updates affecting JSA?

Have weekly rates changed in 2025?
Yes, a 1.7% increase from April 7, 2025.
-
- Under-25 rate = £72.90
- 25+ rate = £92.05
What legal or policy updates should claimants know?
- Waiting days reintroduced as 7-days in October 2025 (up from 3) .
- NI credits (Class 1) continue for new-style claimants—even if benefit is zeroed due to pension or earnings
- Benefit recovery guidance strengthened to ensure DWP can reclaim overpayments effectively, protecting public funds
Conclusion

I’m Adam Milne, a business writer and co-author at UKBusinessMag.co.uk. I’m passionate about simplifying complex topics—whether it’s tax, startup strategy, or digital marketing—so that entrepreneurs can take action with confidence. With years of experience in small business consultancy, I bring a practical perspective to every piece I write, helping readers turn ideas into results.



